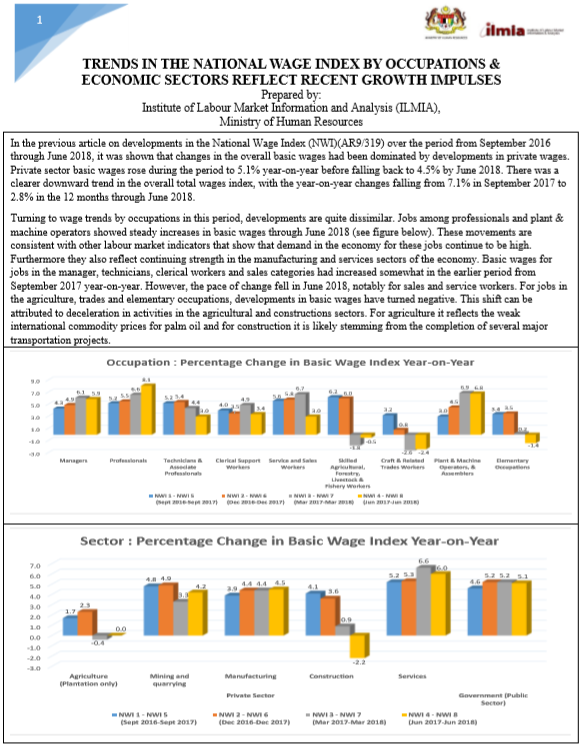
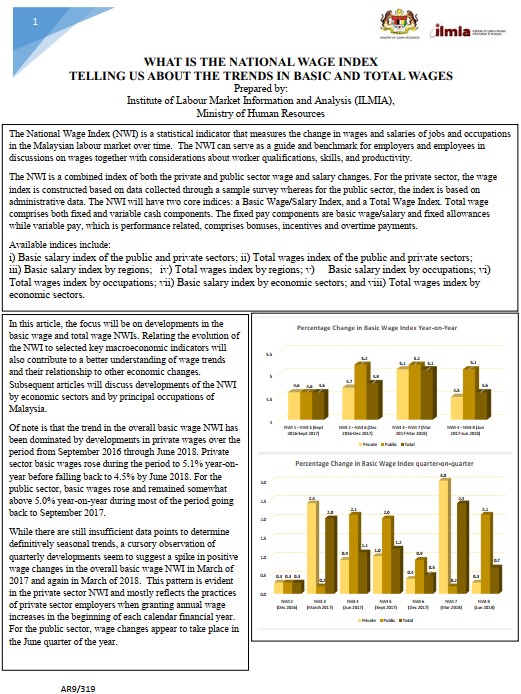
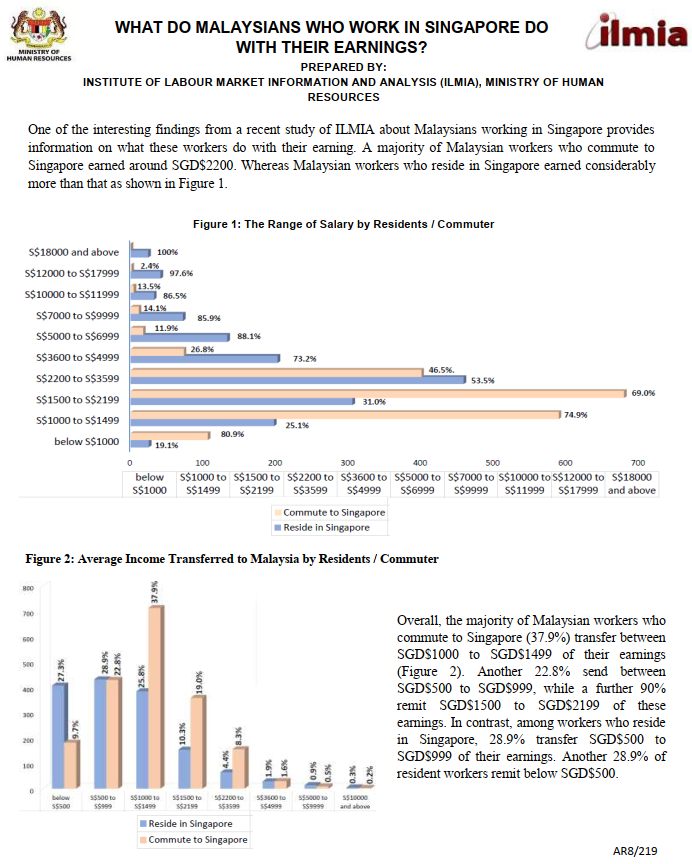
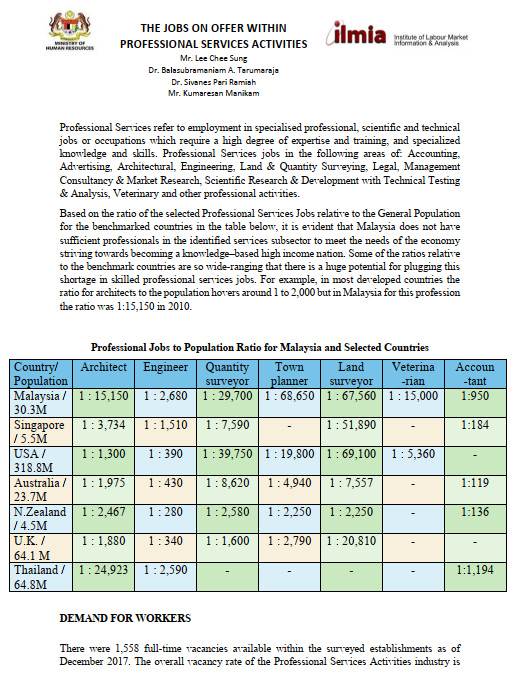
Publication
Following registration, all publications lodged with ILMIA may be accessed, following normal conventions for usage. Accessible ILMIA publications usually include all research projects, studies and products generated as output of work activities. A few ILMIA Publications are indicated as available upon request and could be shared with interested parties on a restricted basis. As ILMIA strives to be the main hub for all labour market related information, some Publications from other government agencies and private organizations are also accessible following respective sharing arrangements. Otherwise links are provided to the respective publishing entity.
ILMIA Publication

Critical Occupations List Report 2018/2019
The CSC is co-chaired by Talent Corporation (TC) and ILMIA within the MITI-led Industry Skills Committee (ISC) established under the Cabinet-level Human Capital Development Council arising from RMK11. The COL forms part of a monitoring framework that will more accurately and continuously inform human capital policies and programs deployed to correct workforce and skills imbalances in the economy. COL 2018/2019 and future updates envisages a widening of coverage of critical jobs to more industries and occupations, including semi-skills positions.
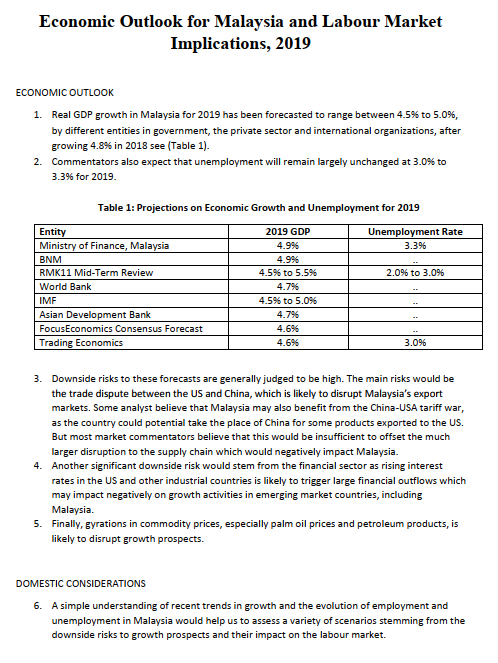
Article: Economic Outlook for Malaysia and Labour Market Implications, 2019

Article: Environmental Scan: Food & Beverages Industry 2018
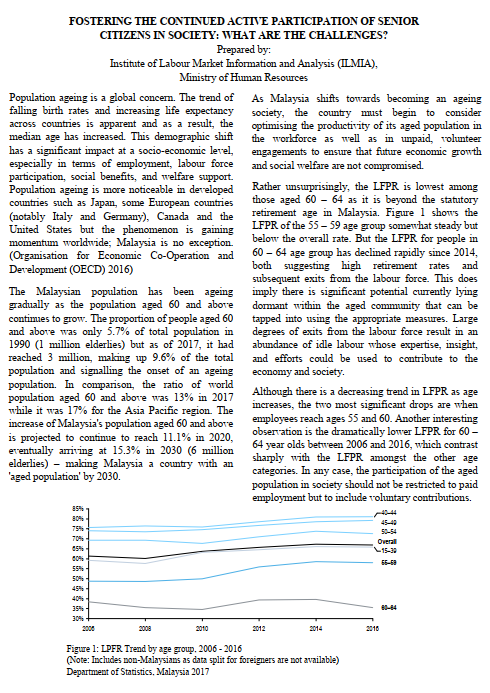
Article: Fostering the Continued Active Participation of Senior Citizens in Society: What are the Challenges?

Article: Malaysians with TVET Qualifications are Essential for Sustaining Economic Growth
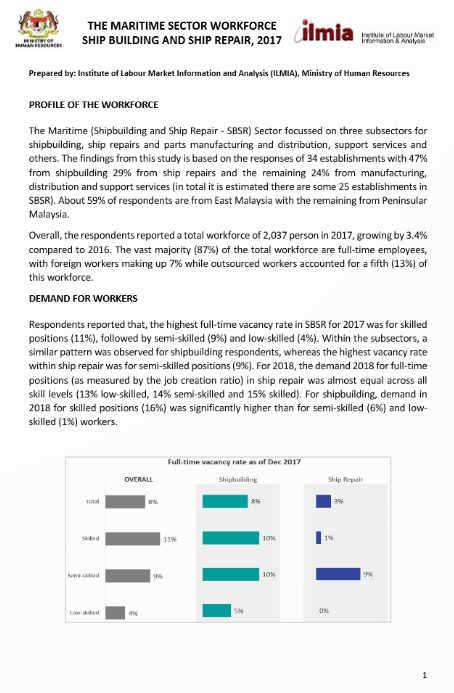
Article: The Maritime Sector Workforce: Ship Building and Ship Repair (2017)

Article: National Employment Returns 2018

Environmental Scan 2018: Human Capital Issues Within Machinery & Equipment and Advanced Engineering Sector (Phase II)
This Environmental Scan on Human Capital Issues within the Machinery & Equipment and Advanced Engineering (ME & AE) industry is a follow up study of the First Environmental Scan undertaken in 2016. The focus of this study is update labour market and industry information in ME & AE sector for 2017. There are 2 main sections in this report, 1) the environmental scan which comprises Introduction, Business Profile, Workforce Profile, Industry Trends and Prospects, Reviewing the Recommendation of the first Environmental Scan, and Strategic Recommendation; 2) the industry workforce survey comprises the Methodology, Workforce Development and Retention Initiatives, Collaboration with Educational and TVET Institutions, and Emerging Trends in ME & AE sector. This environmental scan focuses on 2 major industries which are the Machinery and Equipment (M&E) industry and the Engineering Supporting Industry (ESI). The M & E industry covers 3 sub-sectors, which are (1) specialised M & E for electrical and electronics, (2) specialised M & E for oil & gas, and (3) general M & E for material handling & lifting. The ESI industry covers 4 sub-sectors which are (1) machining, (2) mould, tools and dies, (3) metal casting, and (4) surface engineering & heat treatment.

Critical Occupations List Report 2017/2018
The CSC is co-chaired by Talent Corporation (TC) and ILMIA within the MITI-led Industry Skills Committee (ISC) established under the Cabinet-level Human Capital Development Council arising from RMK11. The COL forms part of a monitoring framework that will more accurately and continuously inform human capital policies and programs deployed to correct workforce and skills imbalances in the economy. COL 2016/2017 and future updates envisages a widening of coverage of critical jobs to more industries and occupations, including semi-skills positions.

Study of Manpower in the Malaysian Logistics Subsector
A study was conducted on the manpower demandand supply in the Malaysian logistics industry under the purview of the Ministry of Human Resources (MoHR) and Ministry of Transport (MoT) Malaysia. The logistics sector is a significant component of the economy, given its role as a key enabler for the other economic sectors in terms of facilitating movement and mobility of goods and in increasing international trade connectivity. This study aims to provide insights into the human capital aspectsof the Malaysian logistics industry, given that manpower skills and competencies are key components in moving the industry forward. This study provides an overview of the industry from the global and domestic perspective, which includes insights on the regional logistics performance and a comparative analysis of leading logistics nations. This is followed by a manpower assessment of the Malaysian logistic industry to identify the issues and challenges, and provide recommendations to address these issues.

Environmental Scan (ES): Human Capital Issues Within Machinery/Equipment & Advanced Engineering Sector
This environmental scan focuses on 3 sub-sectors within the Machinery and Equipment (M&E) industry (specialised M&E for Electrical & Electronics, specialised M&E for Oil & Gas and general M&E for Material Handling & Lifting) and 4 sub-sectors within the Engineering Supporting Industry (ESI) (machining, mould, tools and dies, metal casting and surface engineering & heat treatment). This environmental scan focuses on 3 sub-sectors within the Machinery and Equipment (M&E) industry (specialised M&E for Electrical & Electronics, specialised M&E for Oil & Gas and general M&E for Material Handling & Lifting) and 4 sub-sectors within the Engineering.

Critical Occupations List Report 2016/2017
The CSC is co-chaired by Talent Corporation (TC) and ILMIA within the MITI-led Industry Skills Committee (ISC) established under the Cabinet-level Human Capital Development Council arising from RMK11. The COL forms part of a monitoring framework that will more accurately and continuously inform human capital policies and programs deployed to correct workforce and skills imbalances in the economy. COL 2016/2017 and future updates envisages a widening of coverage of critical jobs to more industries and occupations, including semi-skills positions.

Labour Cost in Malaysia 2016

National Employment Returns 2016

Study on Supply and Demand for Professional Occupations in Meeting the Need of a High Income Economy in 2020
The study on professional occupations aimed at assessing the imbalances in the jobs market, with many critical occupations enduring recurrent shortages amidst emerging surpluses of graduates observed for some professional positions. Ten categories of professional occupations were investigated comprising engineers, surveyors, architects, lawyers, accountants, doctors, dentists, veterinary surgeons, ICT experts and physical, engineering science & computing support technicians. 23 economic sectors and sub-sectors were examined. The study looked at the trends in these occupations, wage & salary developments, up-skilling and re-skilling opportunities for professionals and demand-supply outlook for the selected job types. The recommendations were quite similar to those found in the corridor studies, emphasising the importance of industry-academia collaborations to meet the talent requirements and strengthening programs for up-skilling and re-skilling. There were suggestions on purposeful policies to increase female professional participation rates. The need for improved data systems to better track professional occupations and supply-demand developments was highlighted.

A Study on Human Capital Requirement for the Sarawak Corridor of Renewable Energy (SCORE) and Potential Development for Kota Samarahan with Special Focus on Serian Division
As in the other corridor research, this study examined the human capital requirements associated with development and investment efforts focused on five growth regional nodes within SCORE, but also Kota Samarahan. The five nodes are Tanjung Manis, Mukah, Samalaju, Baram and Tunoh, while for Kota Samarahan the focused on Serian district. The study was to identify human capital supply and demand issues for the specified economic sub-sectors within each regional node and outline good practices and strategies which can be adopted from experience elsewhere to enhance the availability and sustainability of talent for SCORE’s development needs. The largest demand appear to be for semi-skilled workers in the industries covered. Employers preferred fresh graduates with some exposure to the industry thus highlighting the importance of internships and other attachments to the workplace for students at academic, TVET and training institutions. Jobs in heavy industries like aluminium, steel and shipbuilding were perceived to be unattractive. In part this relates to issues of access and cost-of-living related to remoteness of the work location. Critical jobs facing high demand or potential shortages include CNC machinist, heavy vehicle mechanics and tour guides. Greater collaboration between industry and educational and training providers needed to have better integrated talent development of relevance to job requirements and skills. With high demand in semi-skills jobs TVET type educations needs to be promoted to reduce perception of career path unattractiveness.

A Talent Gap Study for the Communications Sector in Malaysia
This study was initiated in 2014 within a partnership arrangement of the Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission (MCMC) and ILMIA to analyse the talent requirements of the Communications Sector. The Malaysian Communications landscape with a penetration of more than 140% has expanded vigorously both by subscriber numbers and in sophistication in service offerings. In the future, further expansion will be driven by the usage of mobile data and broadband (both fixed and mobile). The critical question is whether Malaysia has the right talent strategy in place to deal with these dynamic changes and sustain the growth momentum. The study focused principally on the Telecommunications Sub-sector and assessed current and future manpower issues for wireless and fixed line technologies, information and network security and emerging technologies (like Cloud computing & Big Data analytics) impacting the communications industry. A job classification framework was developed comprising 29 key job families, 139 job roles and 316 technical competencies relevant for the selected focus areas. Current and future talent workforce needs were assessed in the context of industry demand and workers coming from educational and training entities. The telecommunications sector workforce must be adaptable and agile to meet the ever changing dynamic industry trends, pointing to the need for constant re-skilling of workers. Job talents were very varied across each of the focus areas; critical job roles and competencies were identified. Talent management will emphasize exposure in an innovative environment, a structured career path and attractive rewards enhanced by training incentives.

Industrial Engagement On Demand For Skilled Workers
This report set for the proceedings and presentations outcomes of the Industrial Engagement Workshop held 28-29 September 2015 at Sunway Hotel, Kuala Lumpur. This workshop aim to realised core strategies of increasing the development of human capital for the nation’s progress as stated in the 11th Malaysia Plan. The two-day workshop is one of the initiative to identify the requirements, needs and manpower availability in relation to the skill requirement in industry, including new and future skills, skills gaps in the labour market as well as movement and changes of wages and benefit structures. The involvement of various government agencies, industry players in the private sector, employer associations, employee union and non-government bodies present at the workshop will disseminated the information . Therefore, the expertise and experience assembled in the workshop will result in helpful suggestions and new ideas which may be consider by the government.
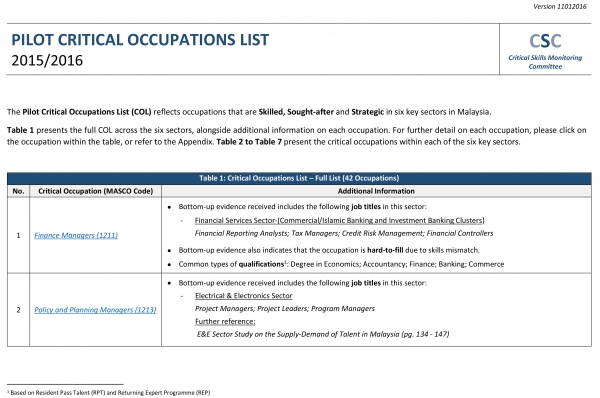
Pilot Critical Occupations List 2015/2016 Report.
The CSC is co-chaired by Talent Corporation (TC) and ILMIA within the MITI-led Industry Skills Committee (ISC) established under the Cabinet-level Human Capital Development Council arising from RMK11. Following the publication of the first COL 2015 (see publications), ongoing follow-on work will contribute to an updated COL 2016 expected to be completed by early 2017. The COL forms part of a monitoring framework that will more accurately and continuously inform human capital policies and programs deployed to correct workforce and skills imbalances in the economy. COL 2015 has thus far been considered for guiding initiatives and providing inputs to University course reviews; Graduate employability training programmes, TC’s Returning Expert Programme (REP), Scholarship management and applications for Residence Pass – Talent (RP-T). COL 2016 and future updates envisages a widening of coverage of critical jobs to more industries and occupations, including semi-skills positions.

A Study Of Developing Skills for Innovation and a High Income Economy in Malaysia
This study examined the requirements in terms of human resources by occupation and skills in each core economic sector in Malaysia. It provides an understanding of how current human resources in Malaysia are contributing to, or constraining, innovation and economic diversification; which characteristics of the labour and product markets affect the incentives of firms to train their workers and of workers to invest in higher level skills; and what are the implications for current education and training systems and for the labour market. The study assessed the current labour market skills gaps and mismatches; addressed policy and institutional settings for skills development and provided a design for a macro-simulation model for policy analysis.

A Study on Human Capital Requirement for Greater Kuala Lumpur / Klang Valley
The Greater KL / Klang Valley study assessed the talent gap and demand-supply of human capital in five industries within the metropolitan region comprising a) transportation, b) shared services outsourcing, c) oil & gas, d) supply chain & distribution, and e) waste & water management. In each of these five industries the focus was on a particular activity which was identified as the driver of future growth prospects within that sector. Thus the study concentrated in (a) on the MRT/ High Speed Rail (Engineering Services); for (b) on Knowledge Process outsourcing (Financial Services); for (c) on Upstream activities; for (d) on Food and Beverage; and for (e) on Environmental consulting. Overall findings included a likely tight supply of graduates for the supply chain and distributive trade areas and possibly a shortfall in supply of semi-skilled TVET related workers in transportation activities. Demand is also likely to outpace supply in environmental green-technology related jobs, especially for entry-level professionals. Recommendations touched on the need to further enhance industry-academia collaborations to meet the talent requirements and to support research and development initiatives to spur innovation, productivity and grow the targeted industries further. Promotion of acceptance of internship among SMEs should be enhanced and a stronger cultivation of upskilling and life-long learning within the workforce should be boosted.

Manpower Requirement Study – Business Services Sector Final Report
This study identified skills requirements in the Business Services sub-sectors; undertook skills gap analysis; proposed strategic issues and policies for human capital development; and put forth an action plan for meeting human resources requirements in the Business Services sector. It assessed issues in several sub-sectors, viz, Aviation Maintenance, Repairs and Overhaul (MRO) and Pure Play Engineering (covering military and commercial services divided into line, component, engine and heavy MRO segments, supplemented by supporting segments); Ship Building/Ship Repair (SBSR cover ships, floating structures, sails, propellers, anchors, maintenance); and Green Technology (GreenTech cover Green Building, Waste Management, and Energy Services Companies (ESCO)). It also analysed critical workforce segments, required skill sets and the manpower supply situation and determined the talent supply pipeline together with best practices in policies to meet skill gaps.

A Study on Human Capital Requirement for the Sabah Development Corridor (SDC)
This study gave an overview of the talent and supply/demand gaps for skilled and semi-skilled labour in four selected sub-sectors in Sabah. It identified talent gaps based on developmental needs and provided benchmarks strategies and best practices from developing and developed nations which can be adopted to ensure sustainable talent within SDC for current and future needs. It outlined human capital issues and initiatives in Sabah, and offered a sector-based human capital supply and demand analysis and key challenges faced by these sub sectors.

Human Capital requirement study for Iskandar Malaysia (IM)
This study looked at the talent landscape in four selected sub sectors in Iskandar Malaysia, namely: Tourism, Creative Industry, Healthcare and Oil and Gas. It identified human capital supply and demand in these sub sectors and highlighted good practises and strategies from other developing and developed nations which can be emulated to ensure sustainability of talent for the corridor development through meeting capital needs. The study gave a broad understanding of the talent landscape within the four sub sectors and also identified the demand and supply for talent and talent requirement gaps. It developed actionable plans for each of the selected sub sectors.

Human Capital requirement study for Northern Corridor Economic Region (NCER)
This study examined the human capital requirement for four selected sub sectors within the NCER, namely, Light Emitting Diode (LED)/Solid State Lighting (SSL), Medical Devices/Technology, Medical Tourism and Cultural Heritage Tourism. It identified human capital supply and demand for each sub sector and outlined good practices and strategies which can be adopted from other developing and developed nations to ensure sustainability of talent for the corridor’s development needs. The study gave a broad understanding of the talent landscape within the four sub sectors and identified talent requirement gaps for each of them. It also formulated actionable plans to ensure sustainable talent in each of these sub sectors.

Study on Wages Structure in The Major Economic Sector Particularly in NKEA's Industries and its Impact Towards Labour Productivity and Capital Intensity
This study analysed the trends and structural changes in wage levels by occupational group in the major sectors including wage differentials between industries, occupational group, education attainment, gender, etc. It examined the impact of wages structure on labour productivity and capital intensity in the economy. It assessed how workers are remunerated for their output and productivity and its benefit to both employers and workers alike that will contribute to Malaysian economic development. It had a special focus on NKEA sectors. Overall the range of the wage structure has widened. Government policies to promote high income have increased wages at the upper end of the wage structure. At the same time, the foreign labour policy has depressed the lower end of the wage structure. Labour competitiveness has been achieved largely by lowering unit labour cost. The labour market appeared to be distorted by a policy of easy supply of low wage labour. Evidence indicated that the Productivity-Linked Wage System (PLWS) in manufacturing has not been effectively practiced.

A Study on Human Resources Manpower Requirement for the Tourism Sector in Malaysia 2012
This study identified skills requirements in the Tourism sub-sectors; undertook skills gap analysis; proposed strategic issues and policies for human capital development; and put forth an action plan for meeting human resources requirements in the Tourism sub-sectors. It assessed issues in 5 sub-sectors, viz, Accommodations (covering 1-5 stars hotels, resorts and guest houses); Tourism Services (covering travel agencies, packaging, booking, ticketing and tour guides); Food and Beverages; Transportation Services (covering taxis, rental cars, bus services); and Retail & Attractions (covering entertainment, sightseeing, shopping, gaming). It included an evaluation of the student demographic profile, learning experience and internship programs to enhance courses and education curriculum to match quality manpower output to tourism sub-sector needs. Some findings were that labour competitiveness has improved as reflected in a decline of unit labour cost from 2002 to 2011. But lower earnings for employees from declining unit labour cost may have reduced attractiveness in hiring and retaining talent. Communications and language knowledge were the main generic skills deficiency areas, followed by customer service skills and hospitality procedures as the main technical deficiencies identified..
A Study Of Manpower Requirement In The Healthcare Sub-Sectors In Malaysia
This study analysed and proposed policies in employment and training requirements for various sub-sectors under the Healthcare Sector in Malaysia. It focused on the manpower demand and supply requirements at sub-sectoral level and identified skills gaps in meeting the requirement for potential new healthcare jobs for the short, medium and long term. It examined the sub sectors of pharmaceutical, medical devices, seniors living and healthcare tourism, and provided a supply and demand analysis as well as a talent gap analysis.
Malaysia Labour Review
The Malaysia Labour Review (MLR) is published biannually by the Institute of Labour Market Information and Analysis (ILMIA), Ministry of Human Resources. It is an academic review dedicated to promoting the study, research and dissemination of information on human resources issues and practices in Malaysia. The journal invites articles on labour management, industrial relations practices, labour economics, employment law, social security and occupational safety and health related issues in Malaysia. The MLR welcomes manuscripts for publication which may be written in either Bahasa Malaysia or English relating to:
- Reports of original research, complete with literature review
- Commentaries on issues of current importance concerning employment
- Opinions on current labour-related events or challenges.
Articles must be original contributions which have not been published elsewhere, in any form, whether in a print medium or on-line and which are not under consideration elsewhere.
Others Publication
 Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu  English
English